Welcome To Trading Insights
Precision Market Insights
Precision Market Insights is the art and science of decoding market behavior through data-driven patterns and price movements. It dives deep into charts, trends, and trading volumes to forecast potential market directions, enabling informed and strategic decision-making. Rather than relying on speculation, it empowers traders with a visual language of the markets—turning numbers into narratives.

Price Reflects All
Price reflects all market factors, while technical analysis focuses solely on price movements—not their causes.

Trends Repeat
Markets follow patterns. Technical analysis identifies these trends, which often repeat and can predict future movements.

History Repeats Itself
Chart patterns recur over time due to consistent human behavior. What worked in the past often works again.
Our Top Educational Sources
Mobile Trading Dubai: Your Guide to Oil Trading
Introduction to Mobile Trading in Dubai...
Read MoreTrading Education Dubai: Ensuring Trading Safety UAE with
Introduction to Trading Education Dubai In...
Read MoreDubai Broker License: Top Forex App UAE for
In the recent past, there has...
Read MoreGuide to Index Investment Dubai, FX Broker UAE,
Explore the Best Strategies for Index...
Read MoreOnline Trading Dubai: How to Invest in Dubai
Online Trading Dubai during the past...
Read MoreDubai Stock Market & Dubai Commodities: Choosing the
One of the biggest and most...
Read MoreOnline Trading in Dubai with Achiever Financials: Benefits,
Online Trading Dubai has become a...
Read MoreStep-by-Step Guide: How to Open a Forex Account
It has never been easier to...
Read MoreAchiever Financials Dubai: Complete Guide to Forex Trading
Dubai often comes to mind when...
Read MoreAchiever Financials Review: Best Forex Broker in Dubai
The world of forex trading is...
Read MoreWhy Achiever Financials is the Most Trusted Forex
The forex market keeps growing in...
Read MoreDubai Stock Market 2025: Online Trading & Equities
The Dubai stock market has entered...
Read MoreHow to Master Currency Trading in Dubai with
Currency trading is one of the...
Read MoreDiscover the Best Forex Education in Dubai with
The forex market is growing rapidly...
Read MoreGold Trading Dubai and Silver Investment Tips from
Dubai remains a global hub for...
Read MoreForex Broker in Dubai: Your Guide to Safe
The financial markets attract thousands of...
Read MoreWhy Achiever Financials is the Go-To FX Broker
Currency trading has become one of...
Read MoreForex Dubai Market Trends 2025: What Traders Need
Dubai is becoming a global centre...
Read MoreA Beginner’s Guide to Currency Trading in Dubai
Currency trading is also known as...
Read MoreStart Currency Trading in Dubai with the Leading
Currency trading has become a popular...
Read MoreWhy Achiever Financials Is a Trusted Forex Broker
More people in Dubai are turning...
Read More
Explore Global Trading Markets
- Trade Forex
- Trade Equities
- Trade Indices
- Trade Commodities
- Trade Precious Metals
The Three Types of Market Trends
Market trends show the general direction of price movement. Recognizing these trends helps traders decide when to enter or exit trades.
Discover Markets – Endless Possibilities

Explore Assets
Maximize Your Potential

Trade Smart
Unlock Global Opportunities

Diverse Assets
One Powerful Platform
Types Of Charts
Line Chart
The simplest form based upon the closing trades forming a homogeneous line. This chart does not show what happened during the time unit selected by the viewer, only closing rates for such time intervals. The line chart is a simple tool for setting up for support and resistance levels.
Types Of Charts
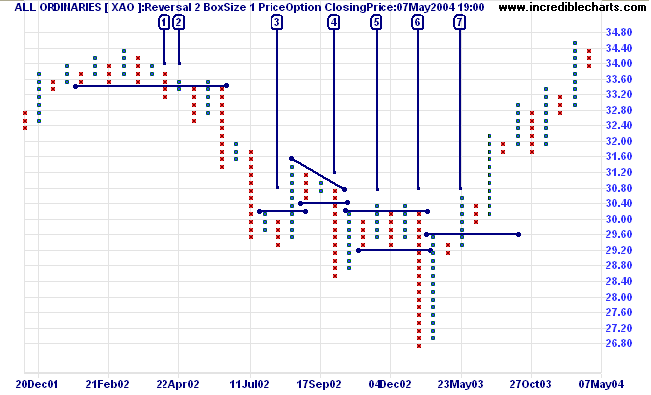
Point and Figure Graph
Chart based on price without time. Unlike most other investment charts, points and figure charts do not present a linear representation of time; instead, they show trends in price.
Types Of Charts
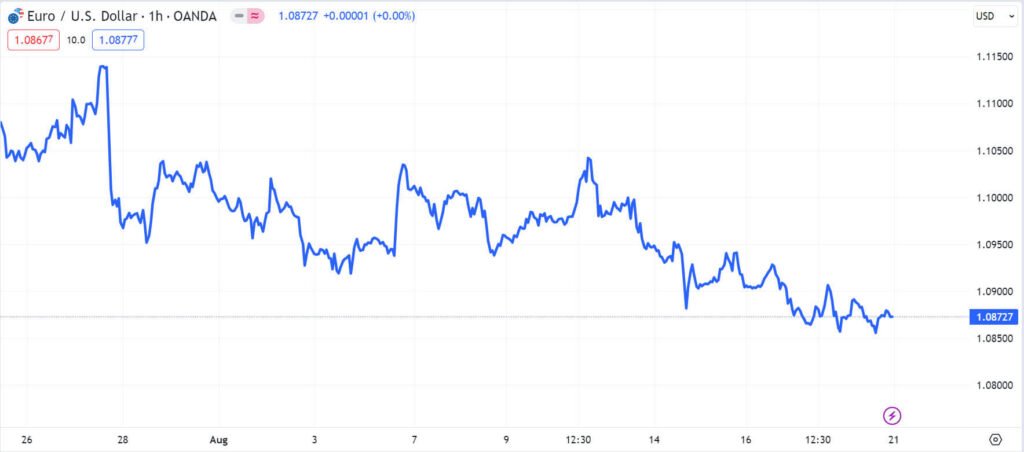
Bar Chart
This chart shows three rates for each time unit selected: the high the low and the closing. This chart provides clearly visible information about trading price range during the trading period; so are popular with many short term traders. Below are examples of a EURUSD bar chart; and a breakdown of one bar below to show what information it contains clearly.
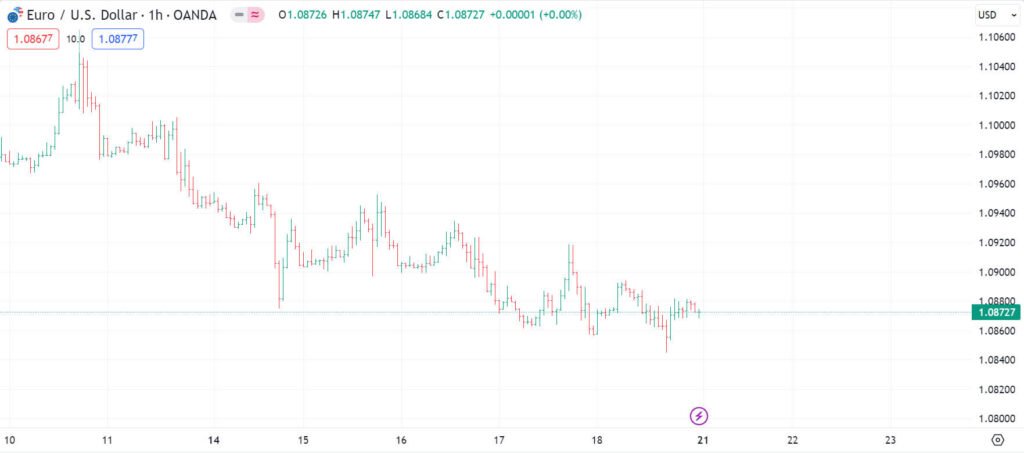
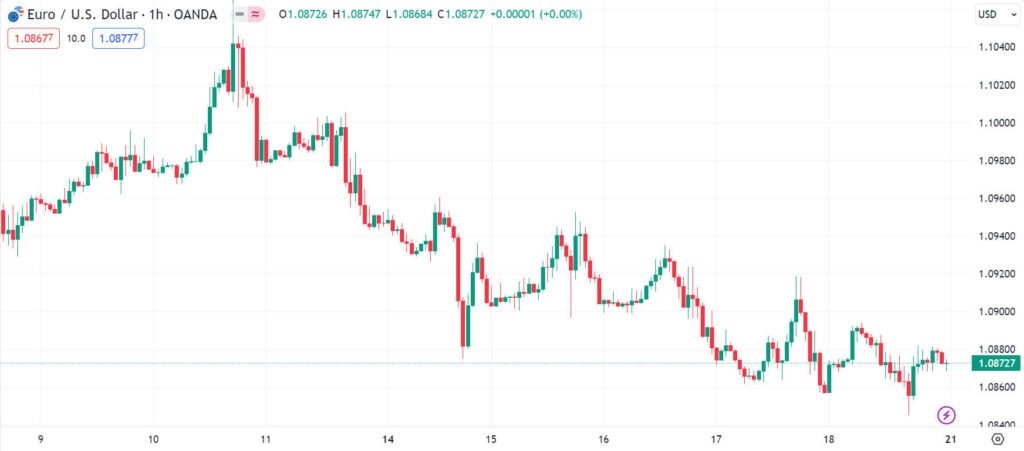
Types Of Charts
Candle Stick
This type of chart represents prices at their opening, high, low and closing prices. Like a bar chart this type of chart contains several key pieces of information and in this case it is represented not as a bar but in the form of candles, for each time frame unit selected. The empty (transparent) candles show an increase, while the dark one shows a decrease. The length of the candle shows the range between opening and closing, while the whole candle shows the whole range of trading prices for the selected unit item.
Trend Lines
A trend line is a sloping line of support or resistance showing the overall direction of price—up, down, or flat.
- Uptrend Line
- Downtrend Line
How traders use trend lines:
- Bounce trades
- Breakout trades
Trend lines help identify short-, intermediate-, and long-term trends.
Trend Lines
Trend Analysis & Timing
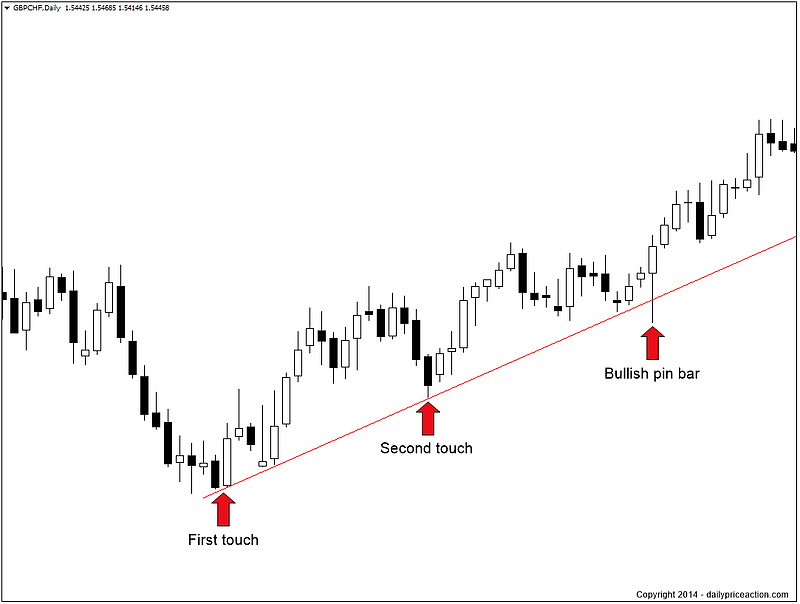
Markets don't move straight up and down. The direction of any market at any time is either Bullish (Up), Bearish (Down) or Neutral (Sideways). Within those trends, markets have countertrend (backing & filling) movements. In a general sense "Markets move in waves", and in order to make money, a trader must catch the wave at the right time.
Trend Lines
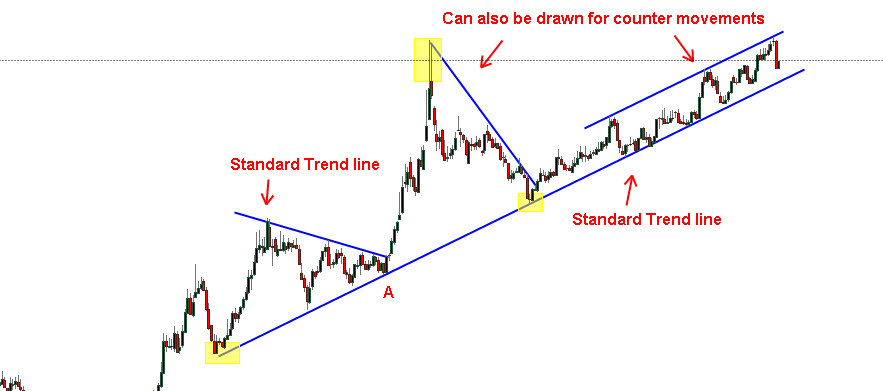
Drawing Trendlines
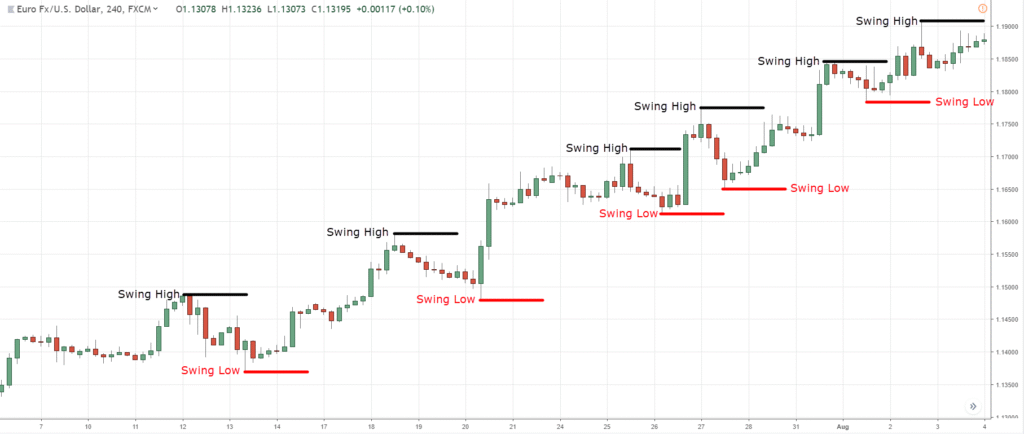
The basic trend line is one of the simplest technical tools employed by the trader, and is also one of the most valuable in any type of technical trading. For an uptrend line to be drawn there must be at least two low points in the graph where the 2nd low point is higher than the first. A price low is the lowest price reached during a counter trend move. Drawing Trend Lines – Below are some examples of annotated charts with trend lines drawn to help guide you:
Trend Lines
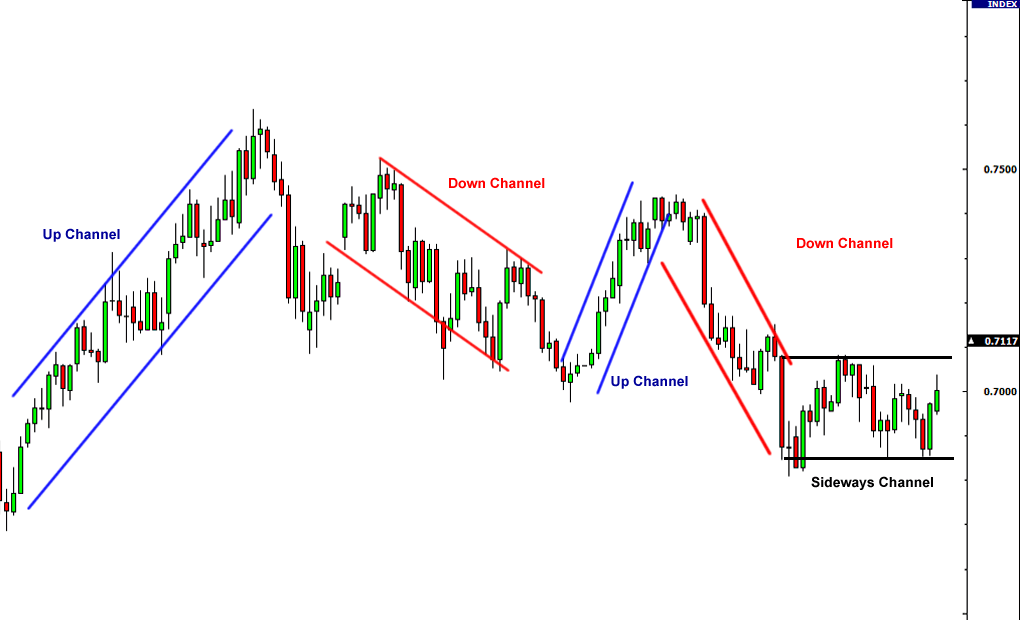
Channels
When price trend between two parallel trend lines they form a channel. When prices hit the bottom trend line this may representative of a buying area and when prices hit the upper trend line this may be representative of selling. Drawing Trend Lines – Below are some examples of annotated charts with trend lines drawn to help guide you:
Trend Lines
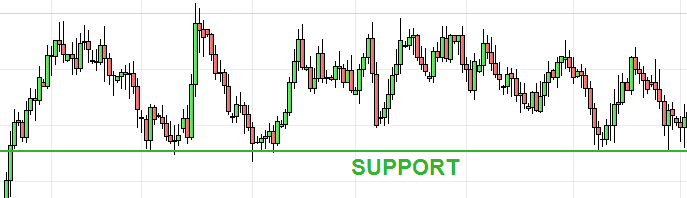
Support
Support is a price level where buying is strong enough to prevent further decline. If price repeatedly fails to drop
below this level, it signals support. Once broken, it
often alerts traders to shift their strategy.
Trend Lines
Resistance
Resistance is where selling pressure stops price from
rising further. Paired with support, it forms a tradable
range until one level breaks, signaling a potential new trend.

Trend Lines
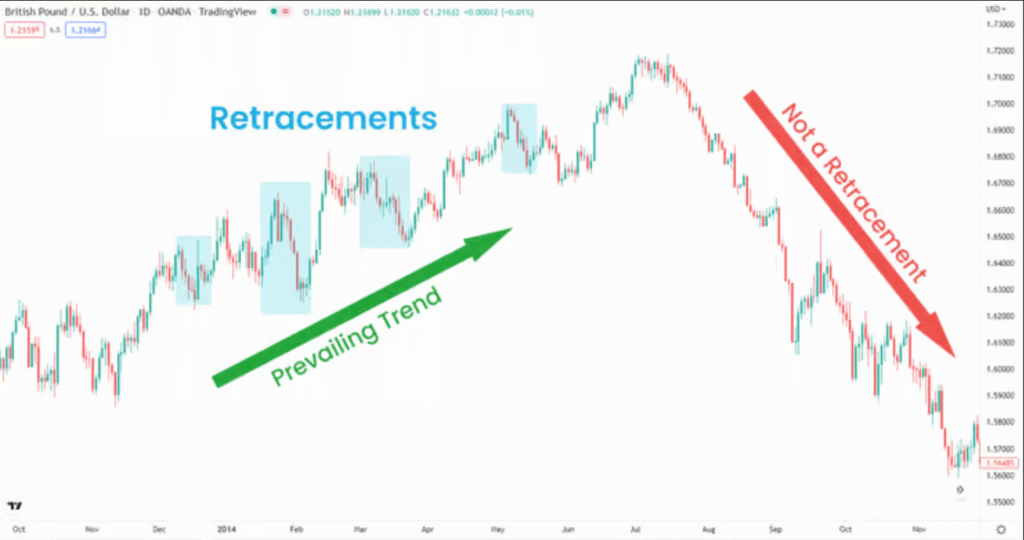
Retracements 50%
Retracements
A retracement is a short-term price reversal against the current trend before continuing in the original direction. Often mistaken for a new trend, it can offer quick opportunities for short-term traders.
Top Forex Indicators
Indicators are key tools in forex trading, helping traders decide when to buy or sell. Essential to technical analysis,
here are the top 8 indicators every trader should know.
Moving Average (MA)
Moving average (MA) is a crucial forex indicator that indicates the average price value over a particular period that has been chosen. If the price trades are above the moving average, it means buyers are controlling the price, and If the price trades are below the moving average, it means sellers are controlling the price. Therefore in trading strategy, a trader should focus on buy trades if the price is above the moving average. The moving average is one of the best forex indicators that every trader should know.
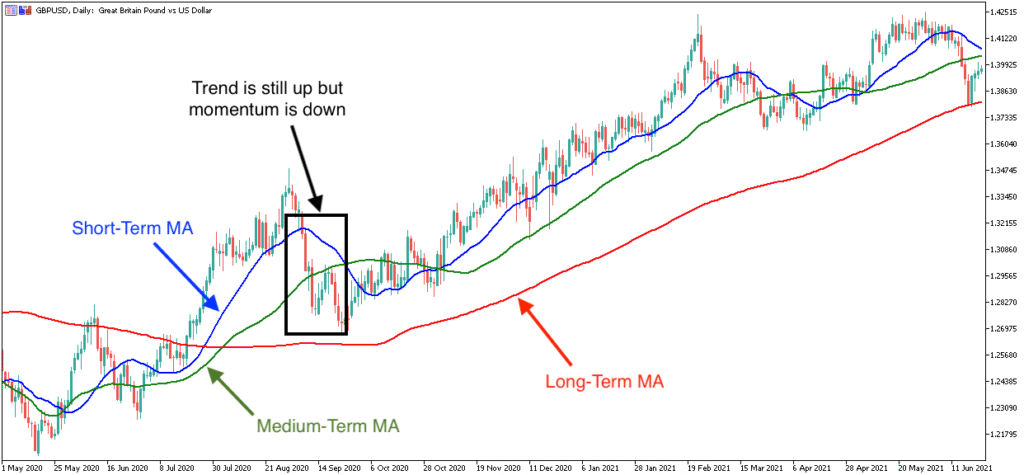
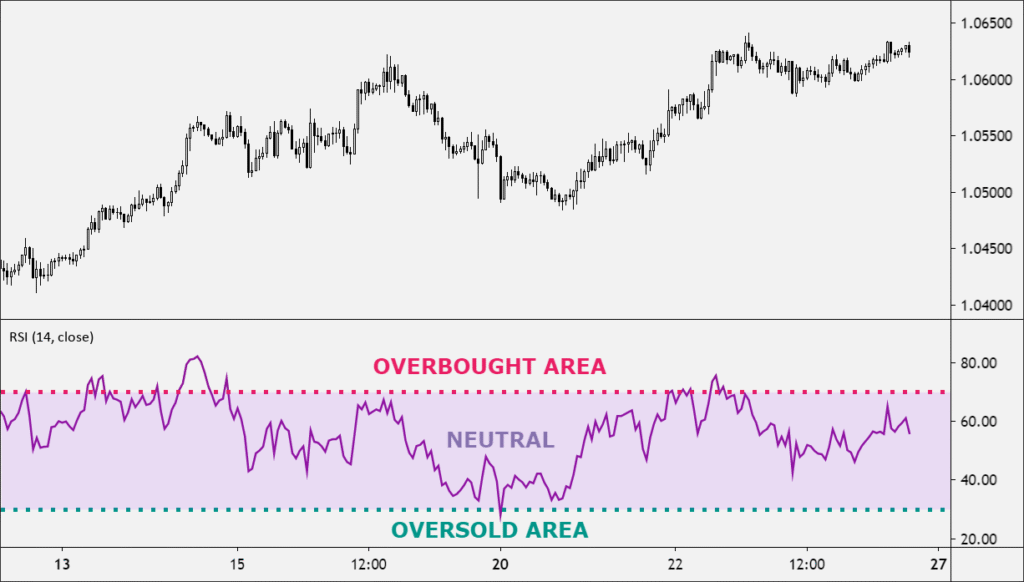
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The RSI is another forex indicator that belongs to the oscillator category. It is known to be the most commonly used forex indicator and showcases an oversold or overbought condition in the market that is temporary. The RSI value of more than 70 shows an overbought market, while a value lower than 30 shows an oversold market. Thus, several traders use 80 RSI value as the reading for overbought conditions and 20 RSI value for the oversold market.
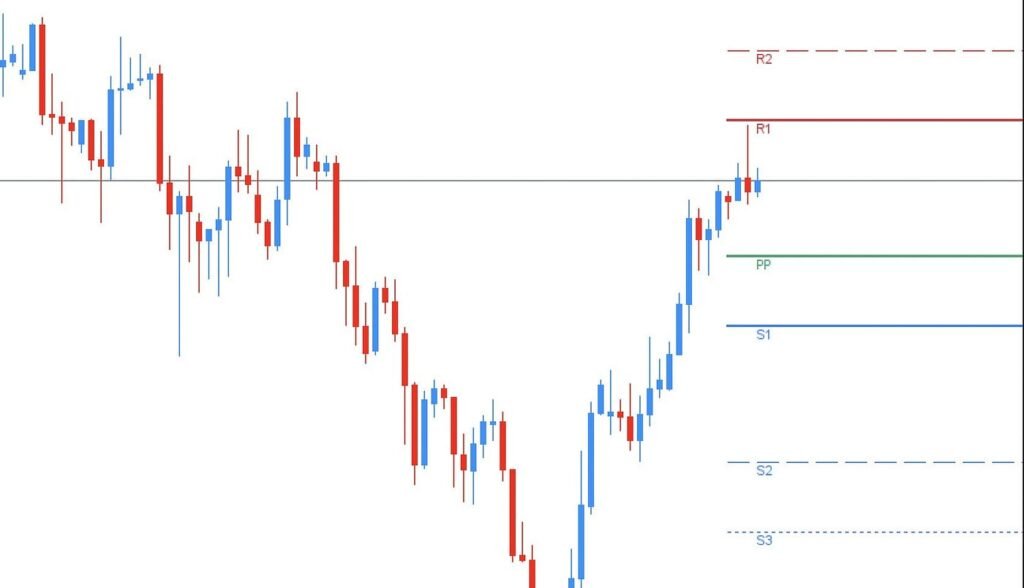
Pivot Point (PP)
This forex indicator showcases the demand-supply balance levels of a pair of currencies. If the price reaches the pivot point level, the demand and supply of that particular paid are at an equal level. If the price crosses the pivot point level, it shows higher demand for a currency pair, and if the price falls below the pivot point level, it shows a higher supply for a currency pair.
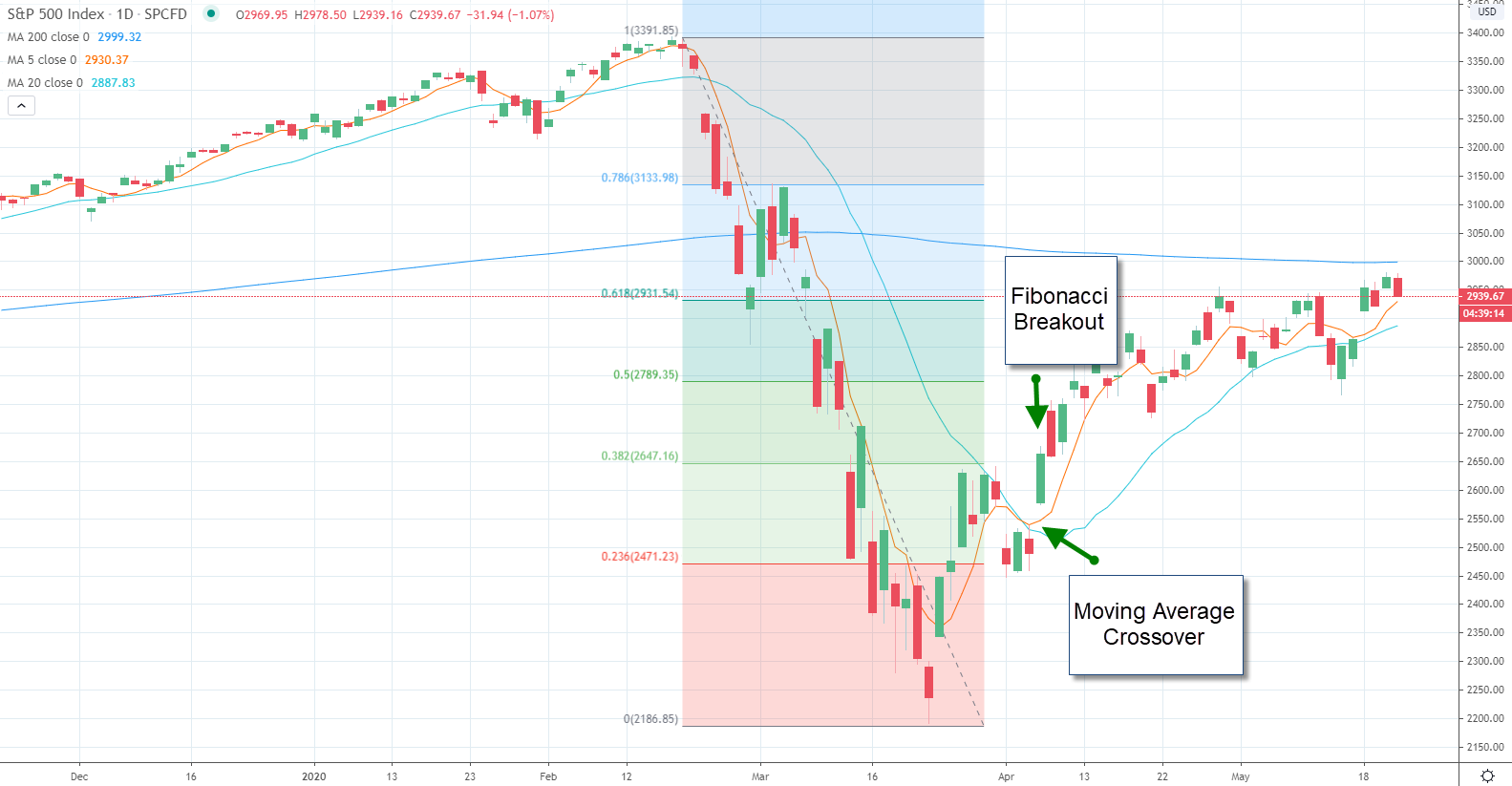
Fibonacci
Fibonacci is another excellent forex indicator that indicates the exact direction of the market, and it is the golden ratio called 1.618. Several forex traders use this tool to identify areas and reversals where profit can be taken easily. Fibonacci levels are computed once the market has made a big move up or down and looks like it has flattened out at some specific price level. The retracement levels of Fibonacci are plotted to find areas to which markets may retrace before moving back to the trend that the movement in the first price has created.
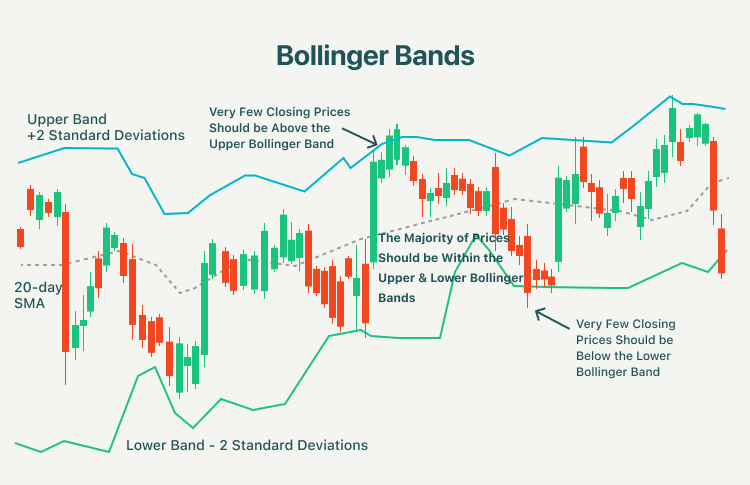
Bollinger Bands
When it comes to measuring the price volatility of a particular security, the Bollinger bands indicator is used to determine the entry and exit points for a trade. Bollinger bands come in three parts, the upper, middle, and lower brands. These bands are often used to determine overbought and oversold conditions. The best part about this indicator is that it helps characterize the price and volatility over time of a financial instrument.
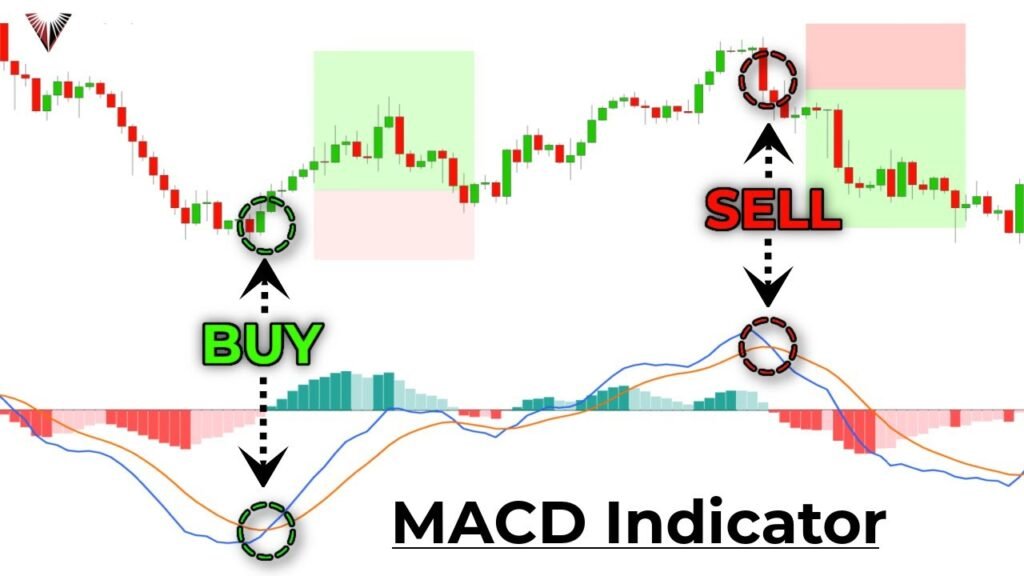
Moving average convergence divergence (MACD)
This is one of those indicators that tell the force that is driving in the forex market. In addition, this indicator helps identify when the market will stop in a particular direction and will go for a correction. MACD is arrived at by deducting the exponential moving average of the long-term from the short-term EMA. EMA is a kind of moving average where the current data gets larger importance. However, the formula of MACD is MACD = 12 Period EMA - 26 Period EMA.
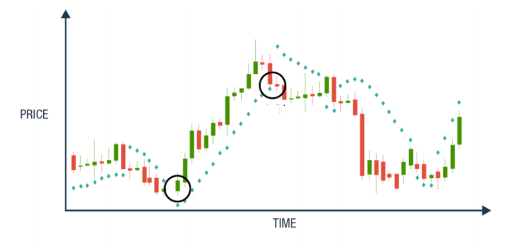
Parabolic SAR
The parabolic stop and reverse (PSAR) is a forex indicator used by forex traders to arrive at the direction of a trend, assess short term reversal points of a price. This indicator is mainly used to find spot entry and exit positions. The PSAR appears as a set of dots on a chart below or above the price of an asset. If the dot is below the price, it indicates that the price is moving up. Conversely, if the dot is over the price, it indicates that the price is moving down.
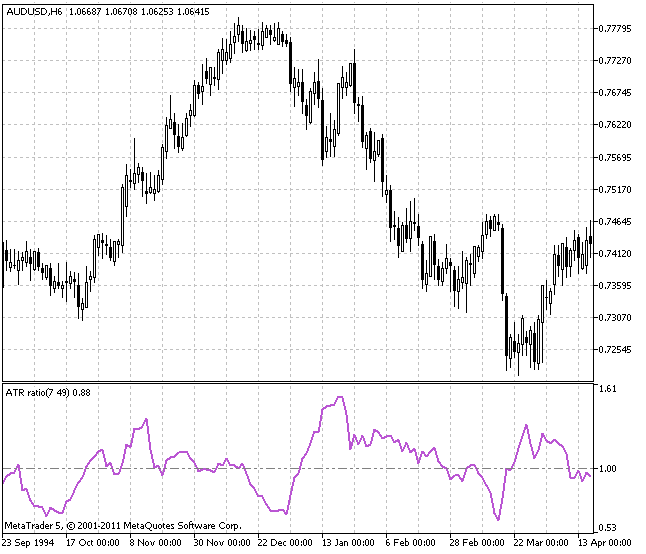
Average True Range (ATR)
The Average True Range indicator is used to measure the market volatility. The key element in this indictor is the range, and the distinction between periodic low and high is called range.
The range can be applied on any trading period, such as intraday or multi-day. In the Average True Range, there is a use of the true range.
True range is the biggest of three measures:
1) Current high to low period
2) Previous close to current high period
3) Prior close to current low period
The absolute value of the biggest of the three ranges is called the true range. However, the average true range (ATR) is the moving average of specific true range values.
We Do It
In all Over the World
We trades in all kind of Stocks, Crypto, Commodities, Metals, Instruments & All kind of
potential assets which will gives the profit











OVER 150K+ CLIENT
Get in Touch
with Us Right Now
Stay connected with seamless updates wherever you trade.